
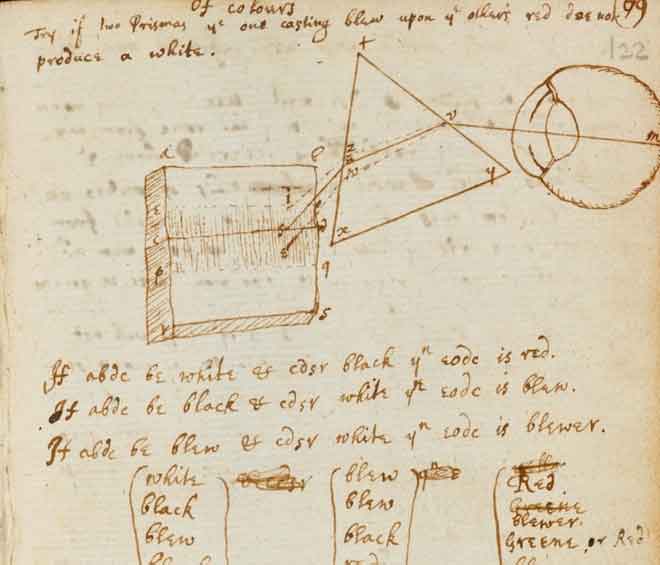
In mathematics, Newton shares the credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of the differential and integral calculus. He also formulated an empirical law of cooling and studied the speed of sound. In optics, he invented the reflecting telescope and developed a theory of colour based on the observation that a prism decomposes white light into a visible spectrum. In mechanics, Newton enunciated the principles of conservation of momentum and angular momentum.
.jpg)

Newton showed that the motions of objects on Earth and of celestial bodies are governed by the same set of natural laws by demonstrating the consistency between Kepler's laws of planetary motion and his theory of gravitation, thus removing the last doubts about heliocentric and advancing the scientific revolution. In this work, Newton described universal gravitation and the three laws of motion, laying the groundwork for classical mechanics, which dominated the scientific view of the physical universe for the next three centuries and is the basis for modern engineering. His Philosophy Naturals Principia Mathematica, published in 1687, is considered to be the most influential book in the history of science. Sir Isaac Newton, FRS (pronounced /ˈnjuːtən/ 4 January 1643 – 31 March 1727 ) was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist and theologian.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
